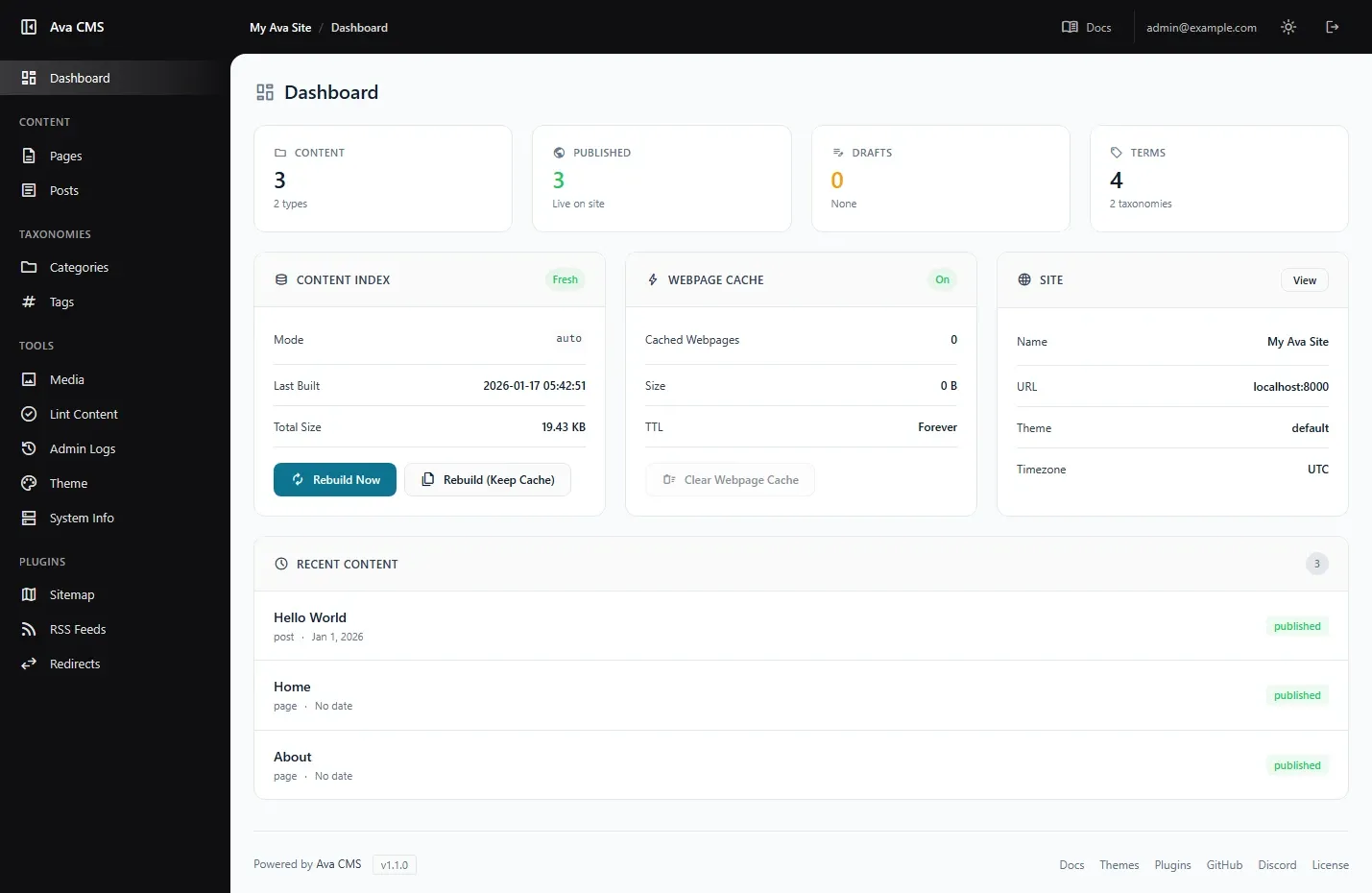
Ava CMS includes an admin dashboard — a complete content management interface that makes working with your site a breeze. Create and edit content with full custom field support, manage media, organize taxonomies, and monitor your site's health.
The admin is especially powerful when working with custom fields — if you have configured advanced custom field arrangements that could be complex to write as raw YAML, you can use simple form inputs with validation, dropdowns, and media pickers.
Getting Started
1. Enable the Dashboard
The admin is disabled by default. Enable it in app/config/ava.php:
'admin' => [
'enabled' => true,
'path' => '/ava-admin',
],
You can change path to any URL (e.g., /dashboard or /manage).
See Configuration for all admin settings.
2. Create a User
Users are stored in a config file (no database). Create one with the CLI:
./ava user:add [email protected] yourpassword "Your Name"
This creates app/config/users.php with a securely hashed password. The file is gitignored by default.
See CLI Reference for all user commands (user:list, user:password, user:delete).
No SSH access? Create users manually
If your host doesn't provide SSH, you have two options:
Option A: Run CLI locally, then upload
Clone your site locally, run ./ava user:add ..., then upload app/config/users.php to your server.
Option B: Create the file manually
Create app/config/users.php:
<?php
declare(strict_types=1);
return [
'[email protected]' => [
'password' => '$2y$12$REPLACE_WITH_BCRYPT_HASH',
'name' => 'Admin',
'created' => '2026-01-12',
],
];
Generate the password hash on any machine with PHP:
php -r 'echo password_hash("your-password", PASSWORD_BCRYPT, ["cost" => 12]), PHP_EOL;'
Copy the output (starts with $2y$12$...) into the password field.
last_login field automatically.
3. Log In
Visit /ava-admin (or your custom path) and log in with your email and password.
Install as an app (PWA)
The admin dashboard supports installation as a basic PWA (Progressive Web App) on mobile and desktop browsers.
That means you can add it to your home screen and launch it like an app:
- Opens in a standalone window (less browser chrome)
- Keeps the admin “pinned” for quick access
- Can cache some admin assets for faster loads
/ava-admin). Your public site remains a normal website.
iPhone / iPad (Safari)
- Open your admin URL in Safari (e.g.
https://example.com/ava-admin). - Tap the Share button.
- Tap Add to Home Screen.
- Launch “Ava Admin” from your home screen.
Android (Chrome)
- Open your admin URL in Chrome.
- Tap the menu (⋮).
- Tap Install app (or Add to Home screen).
Desktop (Chrome / Edge)
Open the admin dashboard, then use the browser’s Install option (often an install icon in the address bar, or ⋮ → Install).
https:// and a supported browser (Safari/Chrome).
Admin Session Security
Session security controls help protect your admin dashboard. Use app/config/ava.php to adjust these settings.
Session Timeout
Admin sessions automatically expire after a period of inactivity. Each page load or action resets the timer.
Configuration: Set via admin.session.timeout.
| Value | Behavior |
|---|---|
1800 |
30 minutes (default) |
900 |
15 minutes (stricter) |
3600 |
1 hour (more lenient) |
null |
No timeout |
IP Binding (Optional)
When enabled, sessions are locked to the IP address used at login. If a session cookie is used from a different IP, the session is invalidated.
Configuration: Set via admin.session.ip_binding.
Default is false (disabled). Enable only if admin users have stable IP addresses.
- Mobile users switching between WiFi and cellular
- VPN users when connections drop or reconnect
- Users behind corporate proxies or load balancers
Features
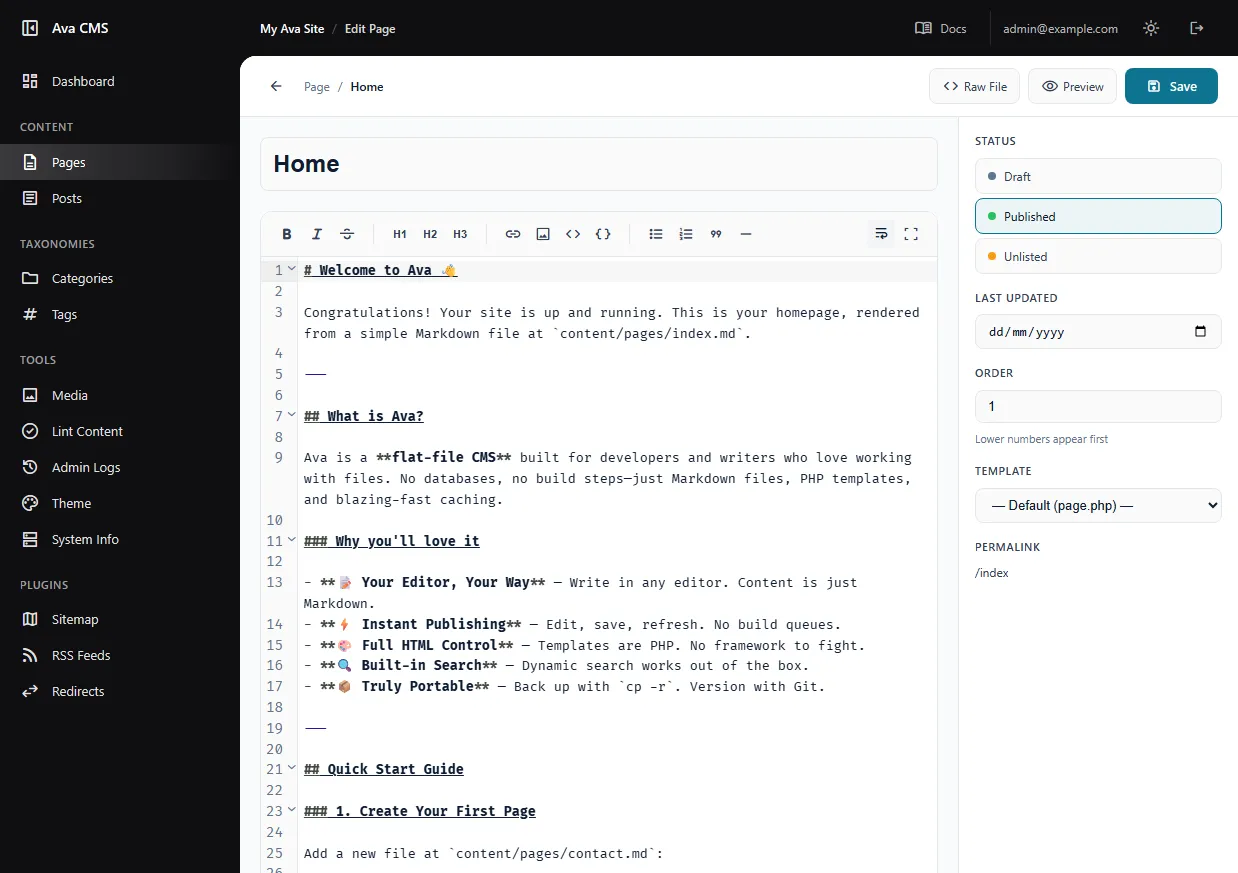
Content Editor
A full-featured content editor with custom field support, syntax highlighting, and live validation.
Browse content by type using the sidebar. Each list shows:
- Title and slug
- Status badge (published/draft)
- Date (for date-sorted content types)
- File path on disk
Create new content with the "+ New" button. The editor generates proper frontmatter and sets up all your custom fields automatically.
Edit with custom fields — This is where the admin really shines. Instead of writing raw YAML, you get:
- Text inputs for strings with character counts
- Date/time pickers for dates
- Dropdowns for select fields and taxonomy terms
- Checkboxes for boolean values
- Image pickers that browse your media library
- Repeaters for arrays and lists
- Real-time validation that catches errors as you type
Syntax-highlighted editor for the Markdown body with frontmatter support.
Preview drafts instantly. Drafts use a preview token so only authorized users can see unpublished content.
See Fields to learn about defining custom fields for your content types.
<script>, <iframe>, and JavaScript event handlers. If you need advanced HTML, edit the file directly on disk.
slug: field. See Hierarchical Content.
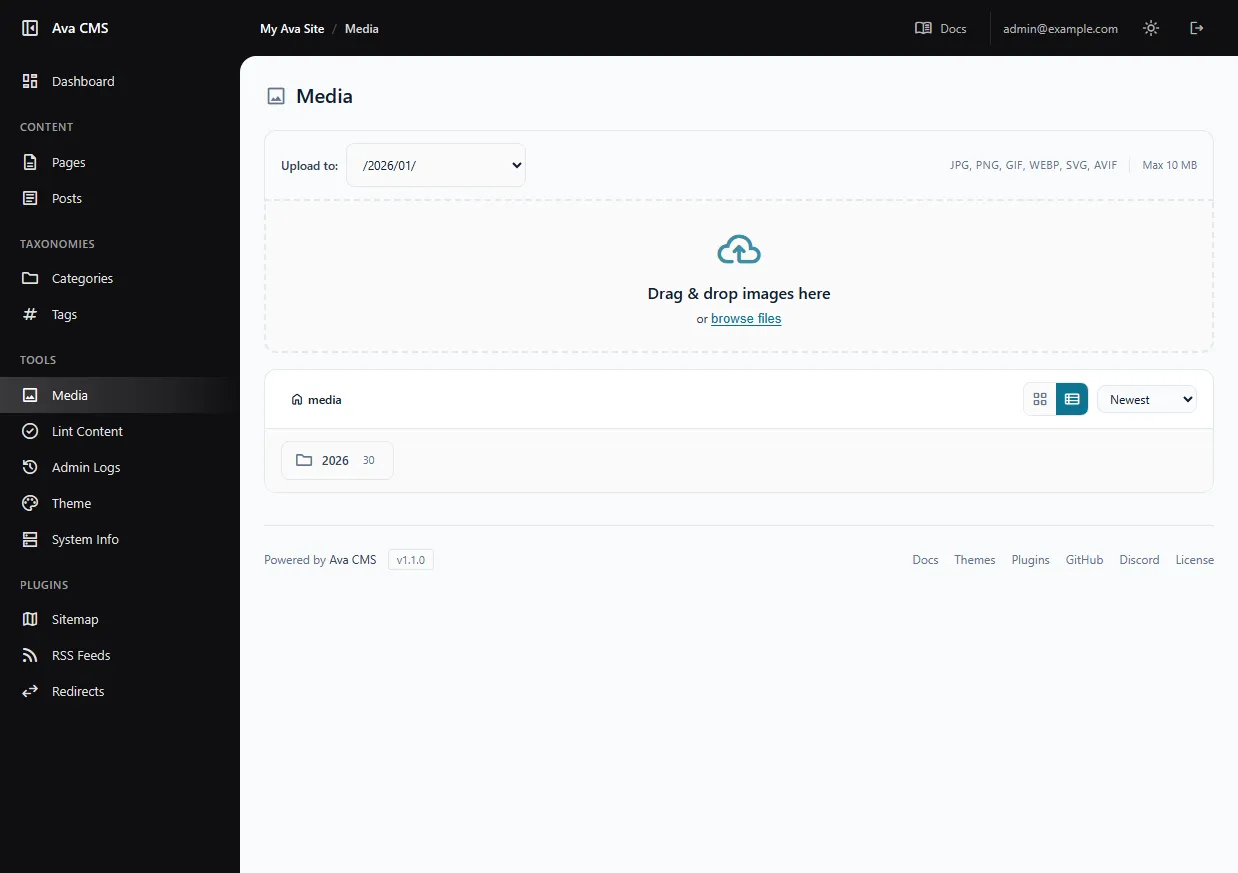
Media Library
Upload and manage images without leaving your browser.
Features:
- Drag & drop images or click to browse
- Folder organization — create subfolders or use automatic date-based organization
- Copy shortlinks — click any image to copy its
/media/filename.jpgpath - Grid or list view — toggle between visual and detailed views
Supported formats: JPG, PNG, GIF, WebP, SVG, AVIF
The upload size limit depends on your PHP configuration — the media page shows your current limits.
imagick or gd PHP extension. Most hosts include these by default.
Taxonomy Management
Create and manage taxonomy terms (categories, tags, topics, etc.) without editing files.
- View terms with content counts per term
- Create new terms with name, slug, and description
- Delete unused terms (terms with content show a warning first)
Terms are stored in content/_taxonomies/{taxonomy}.yml:
- slug: tutorials
name: Tutorials
description: Step-by-step guides
- slug: php
name: PHP
See: Taxonomies for full documentation on configuration, term storage, and template helpers.
Content Linting
Check all your content for errors in one click.
The linter checks for:
- YAML syntax — Valid frontmatter structure
- Required fields — Title, slug, status
- Custom fields — Fields defined in your content type config
- Slug format — URL-safe lowercase alphanumeric
- Unique IDs — No duplicate content IDs across files
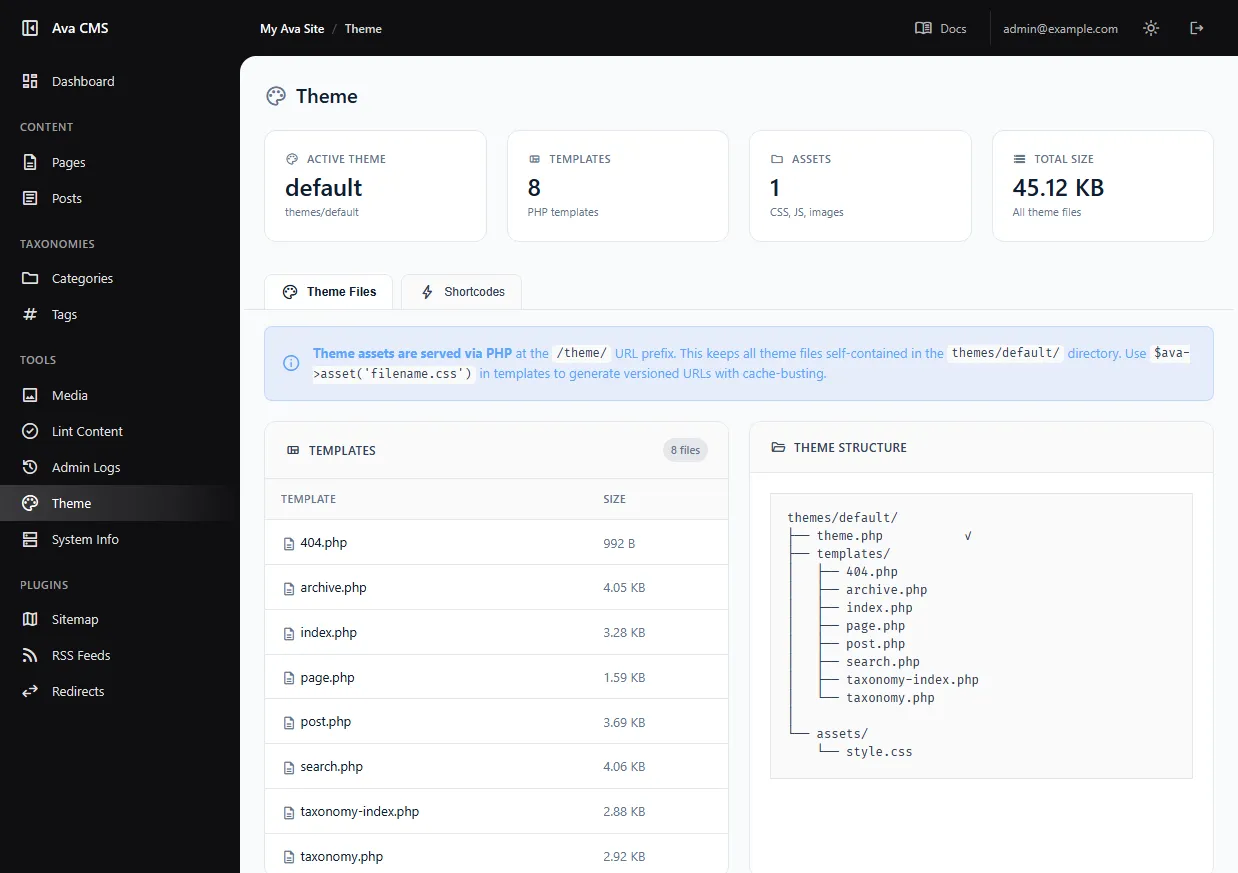
Theme Info
See what's in your active theme at a glance.
- Templates — All PHP template files with line counts
- Assets — CSS, JS, images, and fonts with file sizes
- Shortcodes — Available shortcodes and snippets with copy buttons
See Theming to learn about creating themes.
System Info
Monitor your server and debug issues.
Server stats:
- Disk space usage
- Memory usage (current and peak)
- CPU load average
- Server uptime
PHP info:
- PHP version
- Key extensions (imagick, gd, opcache)
- Memory and upload limits
Debugging:
- Recent PHP errors (with one-click clear)
- Directory permission status
- Cache file details
Admin Logs
Track activity in your admin panel.
- Admin users — List of all users with last login times
- Recent activity — Login/logout events, content changes, system actions
- Security info — IP addresses and browser info for audit trails
Customization
Admin Theme
Choose a color accent for the admin interface in app/config/ava.php:
'admin' => [
'enabled' => true,
'path' => '/ava-admin',
'theme' => 'cyan', // cyan, blue, green, purple, orange, pink
],
The admin automatically respects your system's light/dark mode preference and can be toggled in the top bar.
Extending the Admin
Plugins can extend the admin dashboard with custom pages, sidebar items, and functionality.
What plugins can add:
- Custom pages — Full admin pages with your own UI
- Sidebar items — Links in the admin navigation
- Dashboard widgets — Cards on the main dashboard
- Custom routes — API endpoints for AJAX functionality
Example: The Redirects plugin adds a complete redirect management interface where you can create, edit, and delete URL redirections — all within the admin.
Building an admin page is straightforward:
use Ava\Plugins\Hooks;
Hooks::addFilter('admin.register_pages', function(array $pages) {
$pages['my-plugin'] = [
'label' => 'My Plugin',
'icon' => 'extension',
'handler' => function($request, $app, $controller) {
return $controller->renderPluginPage(
['title' => 'My Plugin'],
'<div class="card"><div class="card-body">Your content</div></div>'
);
},
];
return $pages;
});
See Creating Plugins: Admin Pages for the complete guide.
Security Information
The admin dashboard includes a number of security-related measures intended to reduce common risks, but it should not be considered hardened, independently audited, or production-grade software. The sections below describe current behaviour and design choices, not guarantees of security.
Password Storage
When you create a user with ./ava user:add, Ava CMS currently handles passwords roughly as follows:
- Password hashing — Passwords are processed using PHP’s
password_hash()with bcrypt and a cost factor of 12. - Hash-only storage — The plaintext password is not written to disk; only the resulting hash is stored in
app/config/users.php. - Explicit algorithm choice —
PASSWORD_BCRYPTis used to provide predictable behaviour across supported PHP versions.
What this means in practice: If an attacker gains access to users.php, they obtain a password hash, not the original password. However, hashes can still be attacked using password-guessing techniques, especially if weak or reused passwords are used.
Treat app/config/users.php as sensitive data:
- Restrict access via file permissions, backups, and hosting control panels
- Do not commit the file to version control
- If the file is exposed, assume credentials may be compromised and rotate them promptly
Example stored value (shown for illustration only):
'password' => '$2a$12$erDlkVmb.CvQbJeQoAkwoej1FANMw2QTzf3h2/VI5acJYHcpPagJa'
HTTPS and Transport Security
Hashing protects stored passwords, but it does not protect credentials while they are being transmitted. Without HTTPS, login requests may travel over the network unencrypted and could be intercepted by third parties.
Login & Session Handling
The admin includes several mechanisms intended to reduce common authentication risks, but these should be viewed as defensive measures rather than guarantees.
CSRF Protection
Forms in the admin include a CSRF token intended to help distinguish legitimate requests from cross-site submissions.